In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic exploded and nursing homes rapidly became overwhelmed with disease, death, and despair. During this time, I learned Sylvia, an old woman with dementia I had befriended, was one of the many old and disabled people confined in nursing homes who did not survive. In this reflective and part personal, part scholarly essay, I leave evidence of and for Sylvia and the nearly 200,000 old and disabled people and care workers who contracted COVID-19 and died within the confines of neoliberal, profit-driven long-term care institutions. Disability justice activist Mia Mingus writes, “We must leave evidence. Evidence that we were here, that we existed, that we survived and loved and ached.” Leaving evidence is a political act, a form of resistance in an ableist word. And yet leaving evidence is particularly challenging in the context of dementia, care, confinement, and death—making it even more important, more urgent. Building on Ellen Samuels’ assertion, “Crip time is grief time,” I consider how mourning Sylvia and countless other nursing home deaths, interwoven with my own experiences of distress, yet also solidified my need to survive, might leave evidence and keep working toward an abolitionist future—one in which old and disabled women like Sylvia, like my future self, might thrive.
Keyword: care
Introduction: Crip Pandemic Life: A Tapestry
“Crip Pandemic Life: A Tapestry” takes up a thread from disability justice writer, educator, and organizer Mia Mingus to assemble an archive that “leaves evidence” and captures experience emergent from crip lives and life in the pandemic. The need to gather, hold space for, and preserve evidence—of our angers, our fears, our griefs, our joys, our pleasures, our communities, and our lives—has, for many of us, never felt more urgent. In this editorial introduction to the first installment of the special section of Lateral, “Crip Pandemic Life: A Tapestry,” we narrate project origins in response to pervasive and obfuscating crisis rhetorics, feelings of indignation, and a desire to gather and preserve evidence of crip life and crip knowledge from within the context of the pandemic. “Crip Pandemic Life: A Tapestry” offers a unique digital archive that brings together creative and scholarly reflections to document the experiences of disabled people during the COVID-19 pandemic. The collection includes a multimodal introductory roundtable; multimedia projects; digital renditions of sculptures, masks, fiber arts, and zines; critical interrogations of pandemic politics and policies; and theorizations of crip sociality. This editorial introduction is our brief overview and invitation for readers to travel through spacetimes, bear witness to, and be cared for by this tapestry, archive, collection.
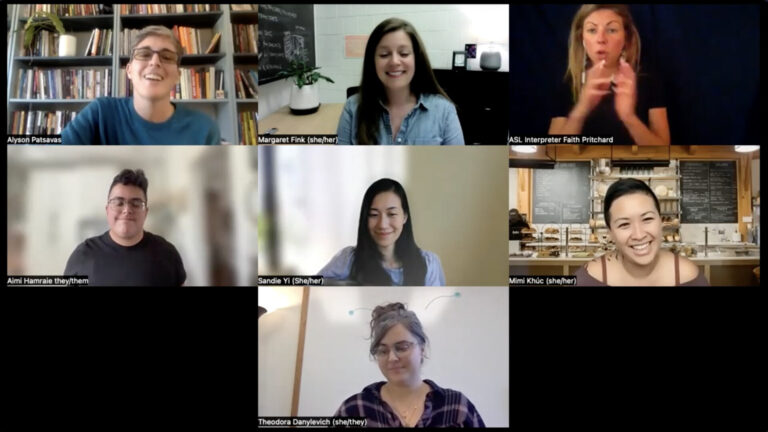
Crip Pandemic Conversation: Textures, Tools, and Recipes
“Crip Pandemic Conversation: Textures, Tools, and Recipes,” brings together experts whose scholarship, curation, organizing and artistic work centers crip insights and creativity to reflect on the work that “Crip Pandemic Life: A Tapestry” undertakes. Margaret Fink, Aimi Hamraie, Mimi Khúc, and Sandie Yi each discuss how the pandemic impacted their work, and they join section co-editors Alyson Patsavas and Theodora Danylevich in discussing the tapestry’s content. Their conversation pulls out some of the most salient threads of the work: smallness, grief, care, community-building, tenderness, and pandemic coping tools. “Crip Pandemic Conversation: Textures, Tools, and Recipes” includes an unedited video recording of a Zoom roundtable session, a lightly edited text version of the conversation, and a glossary of terms that appear in the discussion, as a contextualizing access tool located at the bottom of the document. In choosing a preferred way of engaging with the content, we invite readers to consider, as the roundtable participants themselves do, how access (transcripts, zoom recordings, and captions) produces its own caring archive and knowledge-making practices.
On Navigating Paranoia, Repair, and Ambivalence as Crip Pandemic Affects, Or, I’m So Paranoid, I Think Your COVID Test Is About Me
How do my “hermeneutics of suspicion” color this current crisis? In this auto-theoretical essay, I reflect upon the blend of judgment, suspicion, and paranoia that have settled into my body-mind this past year, and how these feelings shape my engagement with people, institutions, and systems. I have been taught that “judgment” is an essential aspect of immigrant and crip safety. Recently, it has become my (crip)epistemology, and I cannot decide whether this is for better or worse. On the one hand, suspicion is productive. It has kept me and my loved ones alive in a time of deliberate death. On the other, it frustrates, disrupting my capacity for connection. I check my temperature constantly, I hear the guilt in my voice when my family in India tell me they have not left the apartment in months, I spend precious time with friends calculating their risk relative to mine, I go to protests but am afraid of the consequences of my solidarity. Drawing on Eve Sedgwick’s essay on paranoid reading practices, Patricia Stuelke’s Ruse of Repair, Sianne Ngai’s work on ugly feelings, Nikolas Rose’s analyses of somatic ethics, and Mel Chen’s theory of racialized toxins, I explore the modalities that paranoia has both enabled and disabled for me. I examine my ambivalent relationship with repair—some reparative practices like mutual aid sustain queer/crip/immigrant community while others like cure constrict our lives. This piece aims to tease out the tensions latent in crip worldmaking between suspicion and generosity, public health and communal care, and paranoia and repair.
Review of Trans Care by Hil Malatino (University of Minnesota Press)
Hil Malatino’s short book Trans Care critiques the heteronormativity of dominant theorizations of care. By taking trans lives seriously, he shows how trans care webs form the basis of trans survival. Malatino deftly weaves together the insights of trans studies and activism with care feminism to explore the archive, cultural production, healthcare, and politics. He broadens feminist and left perspectives on care and brings care from the margins into the center of trans studies. Trans Care is a plea for stronger, more egalitarian, and solidaristic relations of care.
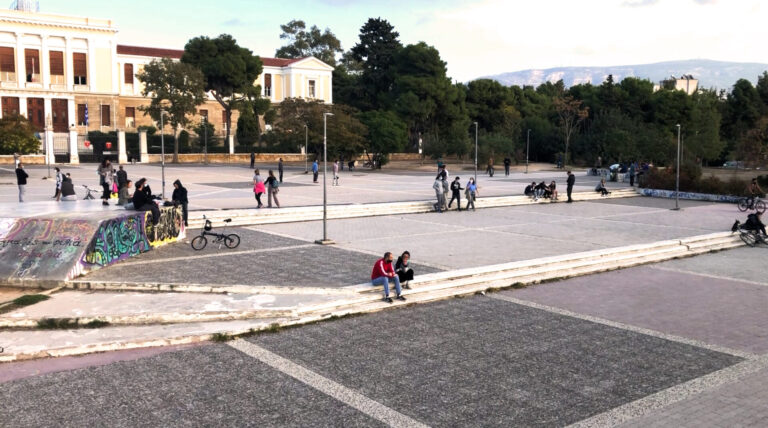
Public Space as Infrastructure of Care: The Affective Dynamics of Protomagias Square During the Pandemic
Our contribution puts forward an examination of public spaces as infrastructures of care. The eruption of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the “social distancing” measures imposed by several governments around the world, transformed the very use and conceptualization of urban public spaces. In Athens, Greece, public space, which had already been in different ways at the forefront of multifarious crises since 2010, reemerged, once again, as a critical site of sociopolitical antagonism. Public spaces, such as squares, became central places where people could come together to share knowledge and emotions, collectively alleviate anxieties, and thus (re)negotiate their positionality in the city. Such formations and enactments of social connection, affectivity, and antagonism, reflect the entanglement between everyday life and the political, and also draw attention to the association of public space with practices of care for collective well-being during precarious times. During the ever-increasing securitization and policing of urban spaces in Athens, in which everyday life has come to be ever more permeated by precarity and uncertainty, public spaces have been reenacted as safe and more inclusive environments where people can be and act together. Our contribution also employs a video to render more intelligible the affective interconnectedness of sounds, images, bodies, materialities, and practices in public space. By attending to the affective dynamics of a public square in central Athens, we examine the entanglements between the sociopolitical production of public space and forms of care during the COVID-19 pandemic.
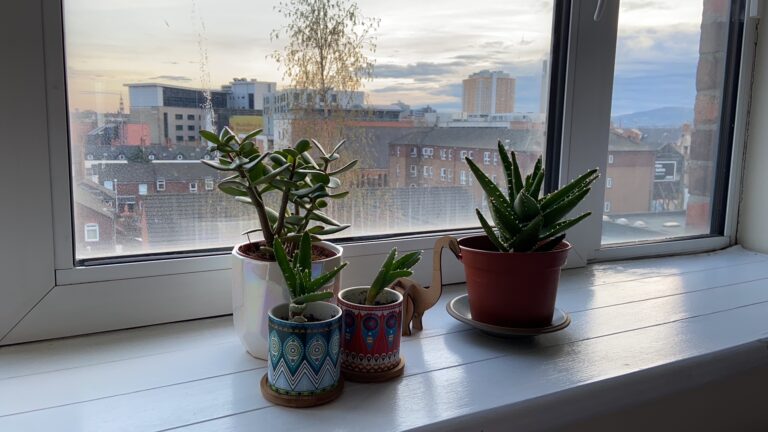
Plants, Vegetables, Lawn: Radical Solidarities in Pandemic Times
This essay presents photos and words illustrating practices of care in homes shared by humans and plants during the COVID-19 pandemic. Drawing on interviews with plant carers, I highlight how humans (re)discovered plants as kin during forced social isolation. I reflect on how plants provided joy, hope, and reassurance during crisis, enabling strong affective bonds with their human carers. I read the creation/cementing of affective bonds between humans and plants for its political significance, and I interrogate the activity of making home/kin with plants as the emergence of interspecies solidarities, which challenge anthropocentric narratives of worldmaking and reinsert non-human beings as central to the making of more just and inclusive futures.
Solidarity in Falling Apart: Toward a Crip, Collectivist, and Justice-Seeking Theory of Feminine Fracture
In this essay, I reconceptualize feminized trauma by utilizing a queer crip feminist disability justice framework. This reconceptualizing allows for an intervention in both historical psychoanalytic and contemporary biomedical framings of the experience of gendered and sexual violence, pursuant or sequelic trauma, and associated symptoms. Both historical and contemporary psycho-logics too often imagine gendered and sexual violence as abnormal or exceptional events (e.g., “stranger rape”) which can be treated and cured individually, thus delimiting them within a white, wealthy or middle-class, cis- and hetero-feminine register. As a corrective, within the framework of everyday emergencies, insidious traumas, and cripistemologies of crisis, I position feminine fracturing and falling apart as chronic, and consider abolitionist strategies for survival, care, and solidarity beyond traditional medical frameworks for recovery. This further provides a way to understand dissociation or rather dissociative-adjacent symptomology as real, legitimate, and painful, yet also as sociopolitical products experienced differently across diverse populations—and as mundane, banal, and even expected for some. Here, feminine fracturing is symptom, method, and potential avenue for change or liberation. What does “recovery” look like when feminized trauma is endemic to the point of being so normalized and unexceptional as to be a thoroughly unremarkable part of our everyday cultural backdrop? How is this exacerbated when we examine the experiences of trans women, poor women, and immigrant and BIPOC women and femmes? I posit that there is promise in embracing a fracturing, in falling apart—as antidote to the normative and neoliberal logic of keeping it together.