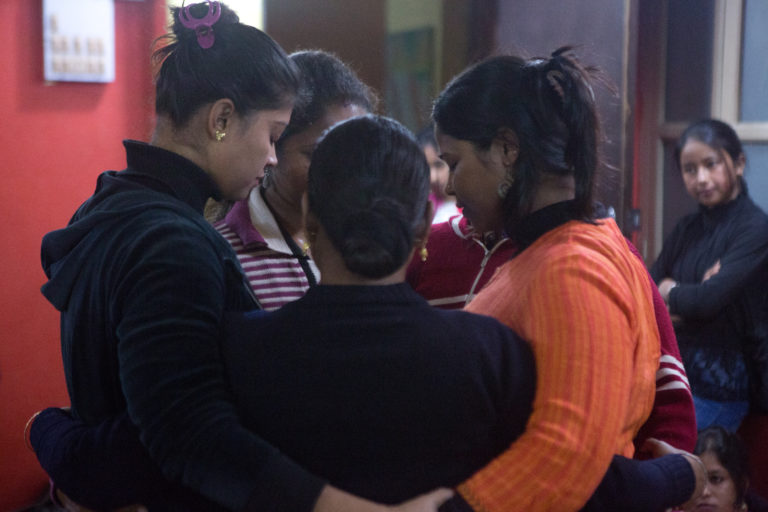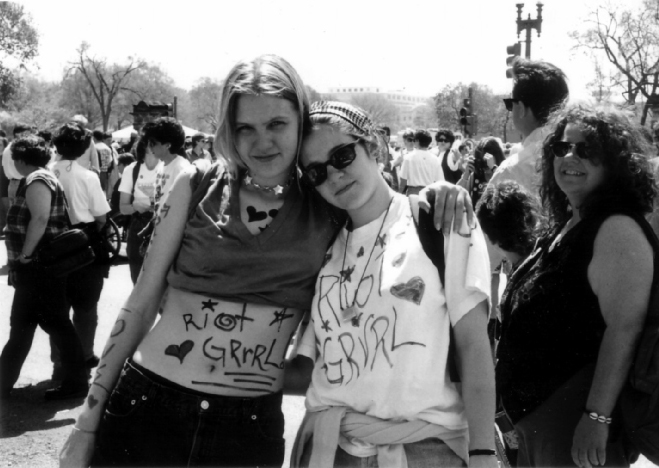When I was rescued by the police and put in a shelter home, I felt angry. I did not know any other work. Before, I just had to lend my body and the work got done. I got paid, without having done anything (Poolish jokhon amake uddhar kore Shelter home e dilo, khoob raag hoechhilo.…
Articles
Peer-reviewed articles in cultural studies.
Beds and Tables: Ordinary Violence in Rascón Banda’s Hotel Juárez
Hotels make for great theatre. They are quintessentially modern (this is especially true of motels, by way of their association with automobiles); they allow for unexpected encounters and mysterious retreats—a clichéd feature of practically every spy drama and tale of illicit sex we can remember; they combine public (lobby, bar, dining room) with private (guest…
Polyrhythms of Citizenship
This talk was presented as a keynote address at the Gendered Citizenship: Manifestations and Performance Conference, January 6, 2015, at the University of Warwick. In this forty-two minute audio-essay, Roy theorizes what she calls polyrhythmic citizenship, the way the intelligibility of the concept of citizenship plays out, much like music, across different contexts and cultures. She discusses “transformative constitutionalism” and “insurgent citizenship” as the component parts of this citizenship, and takes for her key examples the founding of the Indian state and its constitution, and the Delhi gang rape case of 2012 which resulted in the death of Jyoti Singh.
Delhi Dispatches Blogs
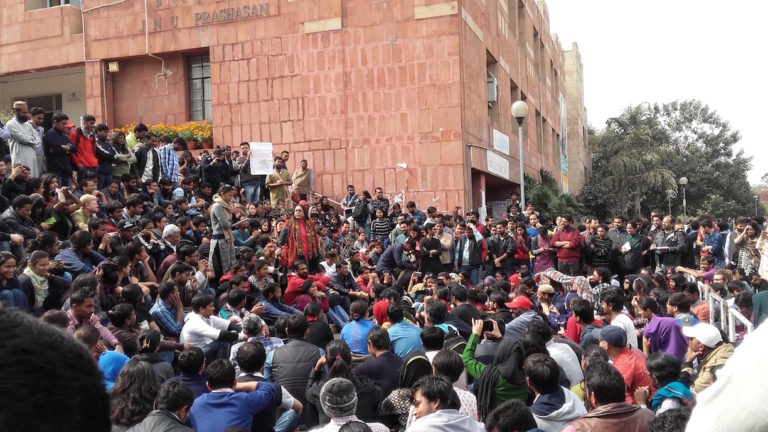
Starting in February 2016, a protracted struggle has taken place on the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) campus, pitting the students and their faculty supporters against the right-wing government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and the Administration of the university. The protestors’ issues chime with the desire to leverage justice that drives this issue. This piece presents one senior scholar and one early career scholar blogging about these events.
Challenges of Praxis: ARM of Care and Kolkata Sanved
As part of our Gendered Citizenship project, we partnered or collaborated with several NGOs and theatre companies whose work is on the front lines of supporting survivors of poverty, violence, statelessness, and homelessness. We have listed these organizations and their websites in our “Further Resources” list at the end of this section. Here we share the “best practices” of two NGOs that work with survivors: one young and community-based (ARM of Care), growing quickly from a grass roots start; the other (Kolkata Sanved) engaged for twenty years to develop a substantial international reputation.
“A Black Man Replies”: Claude McKay’s Challenge to the British Left
Anne Donlon delves into the history of the British Left after World War I to assert the significance of the Black and feminist interventions of Claude McKay and Sylvia Pankhurst. Donlon centers the publication of “A Black Man Replies,” McKay’s letter to the editor published in Pankhurst’s newspaper The Worker’s Dreadnought, against white supremacist logics mobilized by prominent 1920s leftists that contributed to the reestablishment of policing of and violence against black men. Donlon’s archival discoveries weave together biography, material cultural analysis, and histories of trans-Atlantic activism, and, in the process, reveal the labor of building radical intersectional solidarity that came before and followed the moment of “A Black Man Replies.”
From ‘Hip Hop Revolutionaries’ to ‘Terrorist-Thugs’: ‘Blackwashing’ between the Arab Spring and the War on Terror
Rayya El Zein takes up a global analysis of how ideas of blackness, whiteness, and Arabness circulate in post-9/11 media accounts and argues that these concepts work to mediate Western understanding of politics in the Arab world. El Zein unpacks the paradox by which blackwashing is differentially deployed to mark certain Arab subjects as a “good rapper” or a “bad rapper,” and how both of these valences serve to expand neoliberal orientalism through the political familiarity promised by blackness. As an alternative, El Zein suggests attention to the material, historical, and geographic specificities of the power struggles that structure racial capitalism, classism, and racism, especially and essential because of their potential international unrecognizability.
Informatic Labor in the Age of Computational Capital
Jonathan Beller expands conversations about the role of the digital and the digital humanities through attention to the mechanisms by which the digital image is instrumental in neoliberal capitalist accumulation and colonialism. Beller argues that the digital image itself exploits the attentive labor of those who see it, organizes profitable patterns of spectatorship, and links communication directly to financial speculation. Through scrutiny of examples that attempt to disrupt the profitable, algorithmically-capitalized flow of data and attention through the interface of the screen, Beller’s article makes a pointed critique of the ways that fascism manifests in and might be combated via digital economies.
Mixing and Mingling Queerly: The Activist Sociality of Mentoring in the Personal Narratives of Coloma and Lorde
Edward Chamberlain takes on the pressing need for mentorship for queer youth, in particular queer youth of color. Addressing a dearth in both studies on and commitment to the wellness and flourishing of queer youth of color in institutions of higher learning, Chamberlain turns to what is in some respects both a traditional and nontraditional archive of resources: personal narrative writing by queer people of color. Taking up both Audre Lorde’s Zami: A New Spelling of My Name and Roland Sintos Coloma’s “Fragmented Entries, Multiple Selves,” Chamberlain argues that the structural hybridity of these narratives serves as a formal model for a queer mentoring methodology, and delves into the texts themselves for examples of how to mentor queer youth of color in and beyond the academy.
Live from the Nebulizer: Annie Lanzillotto and Eviction Survival
Hillary Miller takes up theories of the city, illness, and precarity via a variety of performances by New Yorker Annie Lanzillotto. Miller argues that as she struggles with survival and eviction in the city, Lanzillotto reveals the bodily and economic limits of the precarious artist while protesting the inequities of the neoliberal city. Through this unique and eloquent study, Miller exposes how neoliberalism acutely and chronically structures the contemporary city’s spaces, socialities, and bodies, and explores performance’s potential and complicity in the face of those structures.
I Can Sell My Body If I Wanna: Riot Grrrl Body Writing and Performing Shameless Feminist Resistance
Leah Perry presents a feminist history of Riot Grrrl and Kathleen Hanna in order to explore the hope and the limits of an individualist revolution in the 1990s. Perry takes on the performance of shamelessness, embodied in Hanna’s songs as well as through bodywriting, sex work, zine production, and other aspects of the riot grrrl movement. Ultimately Perry exposes the position of these performances: they are alternative youth culture for certain subjects which both work against and from within the structures of neoliberalism. Perry concludes that shamelessness might remain a promising space for an urgent anti-racist, feminist politics, if it can work to destabilize power and center women from oppressed groups.
Queer Provisionality: Mapping the Generative Failures of the Transborder Immigrant Tool
Alison Reed investigates the border- and boundary-crossing performance of Electronic Disturbance Theater 2.0’sTransBorder Immigrant Tool (TBT), an incomplete cell phone program that offers GPS, guidance, and poetry to those attempting to cross into the United States across the Mexico/US border. Reed suggests a provocation-based performance of “queer provisionality,” revealing the aesthetics of oppressive power structures by juxtaposing them to social utopias. Interrogating the national neoliberal project of both US liberalism and US conservatism, Reed’s essay is also a transcription of the performances launched around TBT, the social and political machinery set into motion by Electronic Disturbance Theater’s failed utopian project.
Neoliberal Aesthetics: 250 cm Line Tattooed on 6 Paid People
Eunsong Kim challenges existing literature on Spanish artist Santiago Sierra, articulating Sierra’s neoliberal aesthetics as part of a process of managing the imagination of finance capitalism. By situating Sierra’s performance art as a performance of terror, Kim argues that Sierra does not just collaterally reproduce capitalist power relations, but coldly and calculatedly exploits and violates the bodies of the working poor, particularly people of color, for his own profit and for the viewing pleasure of his wealthy audiences. Kim fiercely critiques the ways Sierra profits from his use of Marxist discourse and appeals to political action. In doing so, Kim challenges scholars and artists to embrace the position of laborers and take up Black Radicalism against artistic instantiations of capitalism.
Other People’s Cabins: German Inversions of Onkel Tom’s Hütte
Kristin Moriah’s essay is rooted in extensive archival work in the US and Germany, examining the transatlantic circulation of Uncle Tom’s Cabin through markets of performance and literature in and between Germany and the United States. The essay follows the performative tropes of Uncle Tom’s Cabin from its originary political resonances to the present-day restaurants, train-stops, and housing projects named for the novel. Moriah reveals how the figurations of blackness arising from these texts are foundational to the construction of Germanness and American-German relations in the early 20th century and beyond.
Vibration: Objects Performing Violence, Queerness, and Transcendence / Dick Hungry Whore
Sheila Malone’s work is both digital art piece and critical essay, which explores the queerness of vibrating machines in light of both recent scholarship on objects and materiality and the author’s own work as a performance artist. Malone’s art cuts across and questions the divides between highbrow and lowbrow, permanence and ephemerality, the G-rated and the X-rated. The digital installation and accompanying essay understand the space of inbetweenness as a potential site for queer interventions into existing material orders.