Jose O. Fernandez’s Against Marginalization: Convergences in Black and Latinx Literatures is an innovative project that takes conversations about literary and cultural history in a new direction. Recognizing the efforts of Black and Latinx scholars in crafting distinct literary traditions and histories, Fernandez uses his book to argue for cross-ethnic literary studies and identify similarities between Black and Latinx traditions. This endeavor revolutionizes conversations about literary history of the United States and challenges narratives of exclusion and silencing. This book serves to show the importance of knowing the names of authors and artists, and the communities that fought for them, because they make up the fabric of US history. To learn those names next to Faulkner, Twain, Hemingway, Steinbeck, and Fitzgerald not only makes them part of American literary tradition but also spotlights their absence and exclusion in a way that expands the boundaries of “literary tradition.” This review takes seriously Fernandez’s project, which opens exciting avenues for cross-ethnic historic study while also examining opportunities for future study.
Keyword: United States
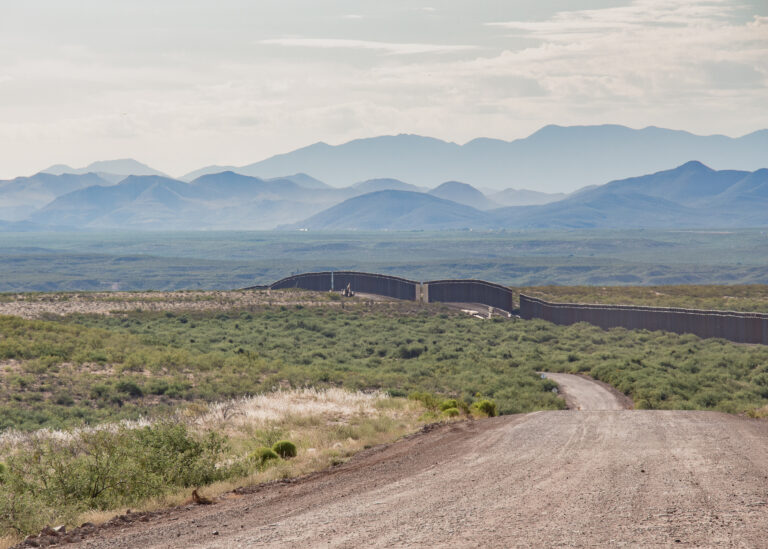
Border Trash: Recovering the Waste of US-Mexico Border Policy in Fatal Migrations and 2666
This article examines how discourses of waste and wastefulness are applied to the bodies of border crossers and border dwellers along the US-Mexico border. Using Josh Begley’s 2016 digital memorial “Fatal Migrations” alongside the fourth section of Roberto Bolaño’s 2666, I examine how the matter of bodies plays an essential role in border policing. Forced into isolated and environmentally hostile areas, migrants are only visible through discarded objects, left behind during border crossing. As a result, American policy and discourse is able to associate migrant bodies with the trash they leave behind—effectively reducing migrant bodies to disgusting and ecologically dangerous. I look at “Fatal Migrations” to consider how the landscape is deployed against migrants and the vibrancy of their bodies after death. This reading leads to a consideration of waste across the border as seen in the fourth section of Roberto Bolaño’s 2666, “The Part about the Crimes.” A fictionalized representation of the feminicides in Ciudad Juarez, Bolaño’s narrative shows the reduction of women’s bodies to capitalistic waste. Taken together the two pieces illustrate the dismissal of bodies to waste and wasteful under overlapping immigration and economic policies. Moreover, both pieces show how death in the borderlands is central to American understandings of sovereignty. The result is increasingly militarized environments and solidified borders in the form of physical structures, cultural attitudes, and policy.
Review of Prison Land: Mapping Carceral Power Across Neoliberal America by Brett Story (University of Minnesota Press)
Brett Story’s Prison Land: Mapping Carceral Power Across Neoliberal America offers a timely reflection on the role of mass incarceration in remaking the neoliberal contours of contemporary U.S. culture. Working within the traditions of critical prison studies and structural critiques of neoliberalism, Story offers detailed portraits of a number of landscapes shaped by the logic of mass incarceration. She persuasively argues that the work of prison abolitionism must also encompass the deeper structural projects of abolishing racism and other injustices in society at large. This book is best read alongside the documentary, The Prison in Twelve Landscapes (2016), by the same author.
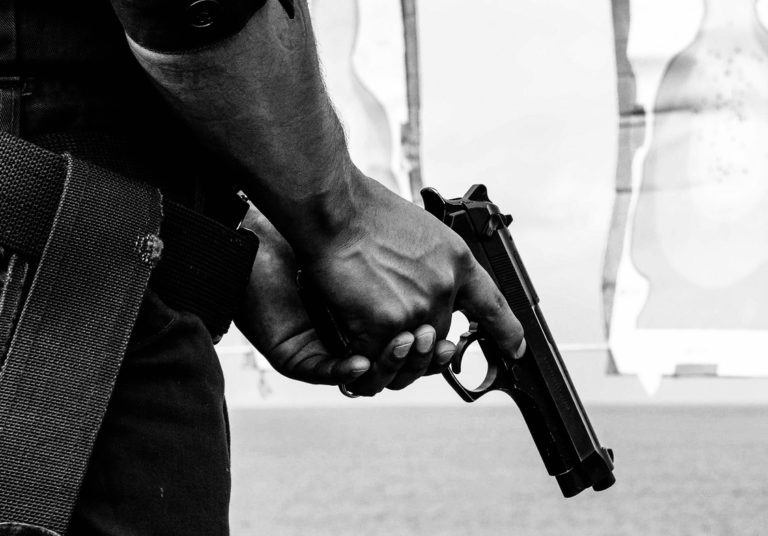
Introduction: US Gun Culture and the Performance of Racial Sovereignty
This introduction examines gun culture in the United States and argues that it is a product of the longstanding practices of settler colonialism, anti-Blackness, and misogyny that have shaped life in the United States. Invoking an anthropological definition of culture, it argues that gun violence is a central facet of US political and social life and that performances of gun use and ownership, particularly when enacted by white men, embody a kind of “racial sovereignty,” or a violent limitation of the practical applicability of citizenship to those who promulgate whiteness, maleness, and violence as primary markers of full belonging in the civic community.
The Self-Defeating Notion of the Sovereign Subject in US Gun Culture
The politicization of U.S. gun culture since the 1970s has popularized the idea that individual freedom and security is dependent upon the reclamation of traditionally defined sovereign powers. In this article, I outline how the exercise of popular sovereignty is a social relation of rule often involving extra-legal forms of violence, which regularizes unequal levels of vulnerability and security among various groups. I then address how the so-called sovereign subject, thought to be at the root of popular sovereignty, is conceptually contradictory and practically self-defeating. In practice, attempts to return to a supposed pre-political condition of personal sovereignty in order to secure individual freedom involves dismantling the very social conditions that enable such freedom in the first place.
On Civil Rights, Armed Citizens®, and Historical Overdose
Today’s radically sovereign Armed Citizen®—a commodity fetish trademarked by the NRA—derives his representational and ethical power from fantasies of self-defensive heroism rooted in historical distortions that obscure the traces of armed settler colonialist violence and racial capitalism. Such historical “overdose” flattens anti-racist civil rights activism, making us “complaisant hostages” of a selective memory that serves self-destructive, necropolitical structures today.
The Necropolitics of Liberty: Sovereignty, Fantasy, and United States Gun Culture
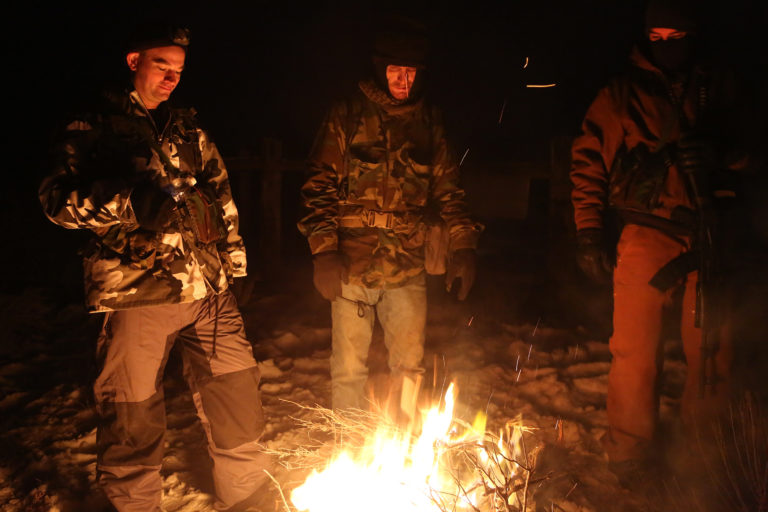
This article approaches the speculative fiction of the survivalist right as an archive that can illuminate the continuities between the fantasies of necropolitical power that animate the radical right and undergird the sovereignty of the United States. Focusing on Malheur National Wildlife Refuge occupier LaVoy Finicum’s 2015 novel Only by Blood and Suffering: Regaining Lost Freedom, this essay argues that such survivalist fiction, in imagining a future civil conflict that enables the reinstatement of Lockean property rights, should be understood as settler colonial rather than anti-statist. In representing the dystopian future in which “public lands” are reopened as a frontier, survivalist novels like Finicum’s reaffirm, rather than challenge, the fantasy that produces the constituted power of the United States.
Good [Black] Guys With Guns: Performance and the Anti-Black Logic of US Gun Culture
This article examines the police shooting of twenty-one-year-old E.J. Bradford at the Riverchase Galleria in Hoover, Alabama on November 22, 2018. After a brief investigation, the Alabama Attorney General’s Office absolved the officer who shot Bradford of any wrongdoing. Through a close reading of the Alabama AG’s report and a performance analysis of Bradford’s actions that night, this article argues that Bradford behaved exactly as he was trained to as a concealed carry permit holder and former enlistee in the Army. Bradford was the epitome of the NRA’s vaunted “good guy with a gun” who intervenes in a violent situation to save others’ lives. However, within the context of the United States’s gun culture, which envisions “good” gun owners as white and encourages police to rehearse responses that perpetuate anti-Black racism, Bradford was always going to be seen by police as suspect.
Review of Empire’s Tracks: Indigenous Nations, Chinese Workers, and the Transcontinental Railroad by Manu Karuka (University of California Press)
Empire’s Tracks: Indigenous Nations, Chinese Workers, and the Transcontinental Railroad by Manu Karuka suggests that the Transcontinental Railroad is a useful lens through which to view issues relating continental imperialism, countersovereignty, and capitalist modes of production.
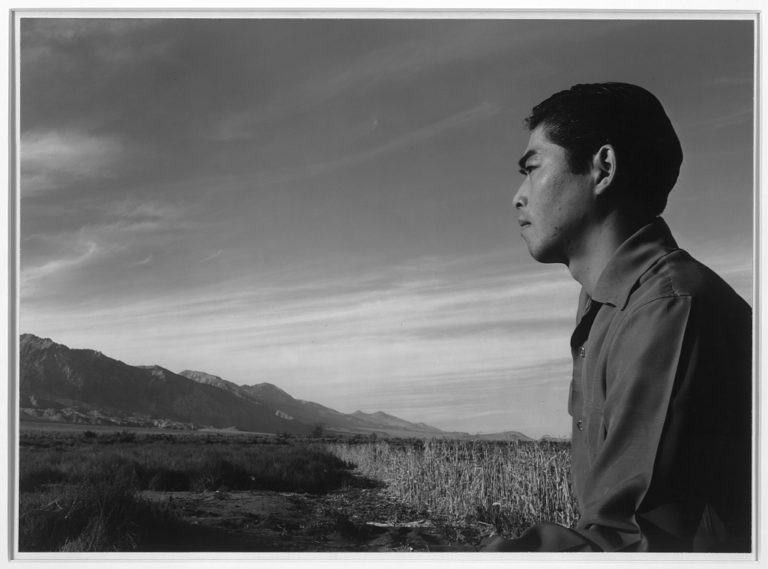
Viewing Japanese Incarceration from Above & Below: Imperial Landscape and Racial Liberalism in Ansel Adams’s Born Free and Equal
This article examines the role of landscape in the visual and narrative representation of Japanese incarceration in Ansel Adams’s Born Free and Equal. Specifically, by analyzing the way it both draws upon and reworks what art historian Albert Boime calls the magisterial and reverential gaze, I argue that Born Free revises the thematic and visual trope of US frontier mythology to articulate a US racial liberal “structure of feeling” in the American century. Born Free oscillates between landscapes and portraits to establish an aestheticized account of frontier nature. In so doing, it forges a vision of racial democracy that can simultaneously “americanize” the Japanese body and universalize US global power. In other words, Born Free’s aestheticized frontier positions the minoritized Japanese body as a national icon that testifies to the racial liberal values of the US, and thus can authorize American (neocolonial) power globally.
Review of Make America Meme Again: The Rhetoric of the Alt-Right by Heather Suzanne Woods & Leslie A. Hahner (Peter Lang)
In Make America Meme Again, Heather Suzanne Woods and Leslie Hahner highlight the central role that memes play in the contemporary political landscape. Specifically, the authors show the ways in which members of the Alt-right have deftly used memes to forward their political agenda, to recruit new members, and to move the so-called “Overton window” rightward to expand the acceptable field of political discourse. In their schema, memes are not simply distractions from important political issues; rather, they function rhetorically and work to constitute the political field. The authors trace the origins of the Alt-right to the murky depths of the internet and show how discourses that emerged from these shadowy depths were able to appeal to a wider audience and cohere around mainstream political discourse. The authors carefully outline the ways that memes circulate, the rhetorical strategies that the Alt-right uses to deploy them, and the ways they work to disavow any charges of racism or extremism that critics might level against them. For Woods and Hahner, memes are the dominant mechanism through which the Alt-right is able to secure and enact its discursive power. Aware of the bleakness of this particular historical moment, Make America Meme Again provides a cogent argument for the ways the Alt-right has been able harness memetic power while also offering a blueprint through which future scholars and activists might reconfigure the present conjuncture so that the Alt-right does not have a stranglehold over the discursive power of memes in the future.
Response to Caroline West’s “From Company Town to Post-Industrial: Inquiry on the Redistribution of Space and Capital with a Universal Basic Income”
This reply critically analyzes the concept of “solidarity” in Caroline West’s account of the role that a Universal Basic Income (UBI) could play in Central Appalachian re-development. I argue that a robust structural form of “solidarity” would necessarily play an essential role in formulating a political bloc capable of implementing an ambitious project like a UBI. In addition to this implicit role of a structural form of solidarity that can connect various communities and constituencies together into a powerful political bloc, Caroline West also articulates an important role for highly local forms of community and solidarity in this region’s transformation. Given the two distinct ways that “solidarity” functions in her account, I raise questions about how the formal features of a UBI relate to both its local and more structural forms.
1983—Stuart Hall Visits Australia and North America
Throughout 1983 Cultural Studies continued to spread outside the United Kingdom, spurred by Stuart Hall’s tour of Australia and parts of the United States where he presented lectures connecting current ideas of what it means to study culture in often disparate and intense political climates across the globe. Myriad publications published in 1983 provide insight into how Cultural Studies circulated among scholars in varying disciplines while still in its infancy. This article situates Cultural Studies primarily within a North American context focusing on the pivotal event of the year: the teaching institute held prior to the 1983 conference at the University of Illinois where Hall delivered what would be eight influential lectures in the field of Cultural Studies. Further, I provide insight into an understudied conference held in Australia where Hall’s impact led to the birth of an Australian Cultural Studies journal. Finally, I provide an overview of some of the pivotal publications of the year, connecting ideas of hegemony, power and dominance, reflexivity and Marxism within a western context.
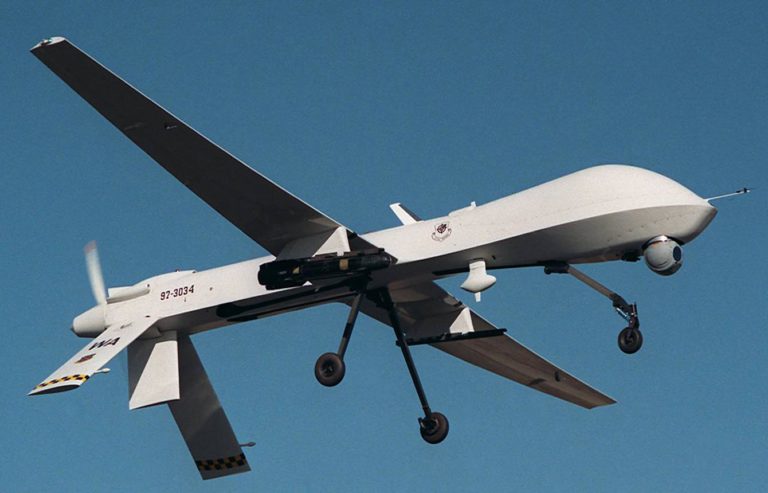
Killer Drones, Legal Ethics, and the Inconvenient Referent
I offer a close reading of the legal and political discourses by means of which the United States government recently has sought to legitimate its use of weaponized drones to carry out targeted assassinations of suspected anti-U.S. combatants abroad. Situating my analysis in the context of philosophical approaches to the problem of truth and linguistic reference, I examine official government speeches, legal documents, and reports of civilian casualties. My semiological critique of these texts is carried out both within and against the “humanitarian” framework of just war theory, my dual approach being necessitated by the twofold strategy of the government’s justificatory rhetoric: on the one hand, the government’s public discourse distorts the accepted meaning of certain unambiguous and pragmatically functional legal signifiers (the jus ad bellum use of terms such as self-defense, imminence, and necessity, for example); on the other hand, it exploits the uncertainty that is endemic to some of those very same terms (necessity and proportionality in particular) when they are used to refer to the jus in bello quantification and valuation of incommensurable variables—of, typically, a particular number of civilian casualties relative to the amount of “military advantage” to be derived from the attack that “unintentionally” produces those casualties.
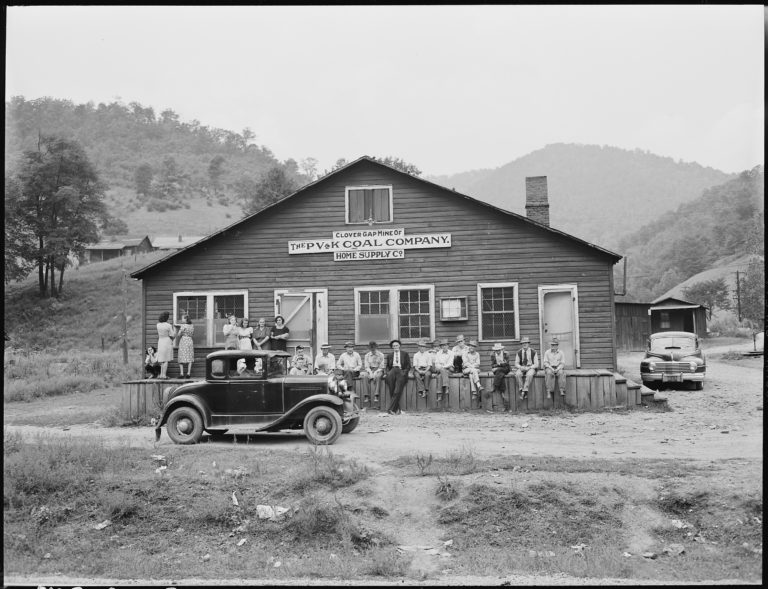
From Company Town to Post-Industrial: Inquiry on the Redistribution of Space and Capital with a Universal Basic Income
This paper considers what effects a universal basic income could have on disrupting social and economic inequality in the tensions of urban/rural divide. She frames her inquiry on the political economy of land and labor in the collapse of coal industry “company towns” and its structural aftermath in Central Appalachia.