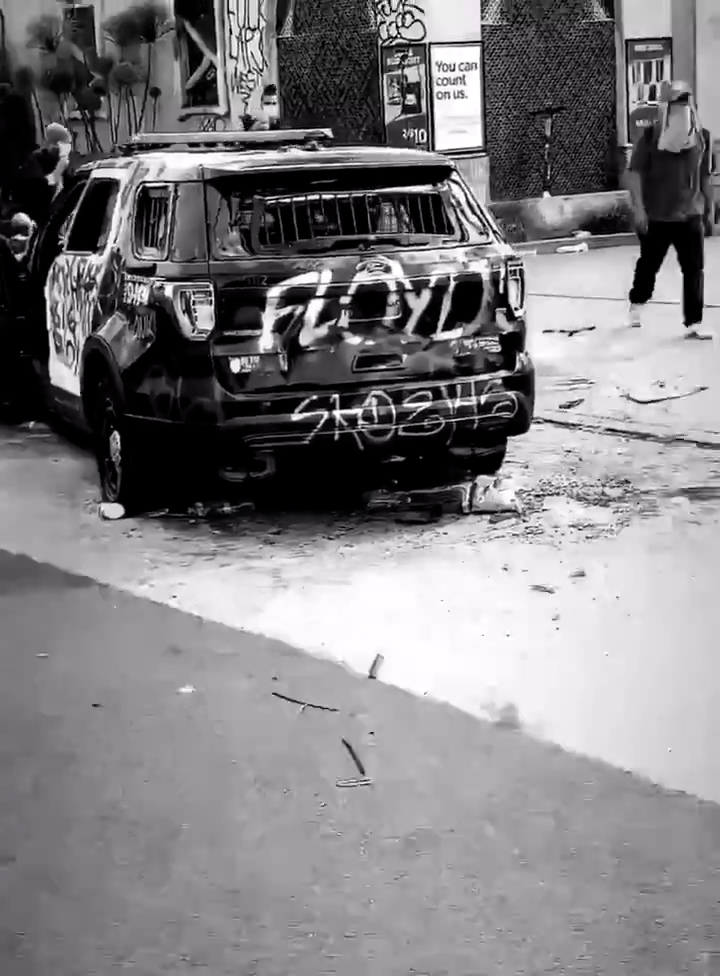
In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, the murder of George Floyd by Minneapolis police has sparked protests and riots around the world. The policing of the pandemic reveals the racial biases inherent to law enforcement and state-led discipline, laying bare ongoing infrastructural inequalities that render racialized subjects more vulnerable to premature death at the hands of police and public health systems alike. With the video embedded in the article, we guide readers through thirty-nine seconds of rioting in Los Angeles on May 31, 2020, shot on a mobile phone and circulated virally on Twitter. The affected body of the witness indexes both the intensity of the event and the embodied experience of the witness, establishing a relation between the two. The experiential aesthetics of the video exceeds the content and this affectivity circulates with its mediation and movement through networked platforms. Such forms of affective witnessing allow for an attunement to political struggle that occurs through what Hortense Spillers would call the analytic of the flesh. Thinking at the intersection of Black studies, affect theory, and media studies, we argue that the flesh is an affective register crucial to the building of global anti-racist solidarities towards abolition.
Keyword: Los Angeles
Review of Tehrangeles Dreaming: Intimacy and Imagination in Southern California Iranian Pop Music by Farzaneh Hemmasi (Duke Press)
Tehrangeles Dreaming is the first book about the Tehrangeles music industry, that is, the Iranian diaspora music industry brought to life by the expatriate Iranian artists and music producers who settled in Los Angeles and Southern California after the 1979 Iranian revolution. Farzaneh Hemmasi uses an ethnographic approach in combination with an analysis of diaspora media discourse in order to “examine expatriate imaginations of influence on, and intimacy with, their global Iranian audiences” (26). At its core, the book deals with the imagining and reimagining of Iranian identity by the artistic community that creates music and media content for Iranians in Iran and across the world.
Dance, Real Estate, and Institutional Critique: Reconsidering Glorya Kaufman’s Dance Philanthropy in Los Angeles
Glorya Kaufman, a philanthropist with a keen interest in dance, has given significant financial resources in recent years to support dance at universities and theaters in Los Angeles. Kaufman’s dance patronage is enabled by a fortune amassed by her late husband. Along with Eli Broad, Donald Bruce Kaufman co-founded Kaufman & Broad in 1957, which became a major purveyor of housing subdivisions in the United States and abroad. In this article, I contextualize Kaufman’s philanthropy within the processes that generated her wealth and the economic role that suburbanization played in the post-war period. In distinction to celebratory narratives that extol patronage for dance, a Marxist analysis of Kaufman’s philanthropy reveals the material connections between concert dance and real estate development. By de-obscuring the source of Kaufman’s wealth, I show how dance funding is bound up in the history of white flight, urban redevelopment, and real estate schemes in Southern California. Practices of institutional critique might prove useful for rethinking Kaufman’s gifts and the political functions of dance patronage.
Review of Civil Racism: The 1992 Los Angeles Rebellion and The Crisis of Racial Burnout by Lynn Mie Itagaki (University of Minnesota Press)
Lynn Mie Itagaki contributes to cultural and comparative race studies by uncovering the implications of what she calls the 1992 Los Angeles Rebellion—a constellation of events spurned on by the Rodney King verdict—for intersecting groups and communities including women, immigrants, Black, Asians, and Latina/o-Americans. Each chapter provides a different context (family, education, neighborhood) for structures and discourses that perpetuate civil racism, while at the same time illuminating specific acts of resistance and subversion that occur, in each instance, through media, activism, and art. Itagaki’s methodology moves beyond critical literary analysis to provide important social commentary and critique that will prove useful to interdisciplinary scholars seeking to learn about racial formations in the neoliberal U.S. context.
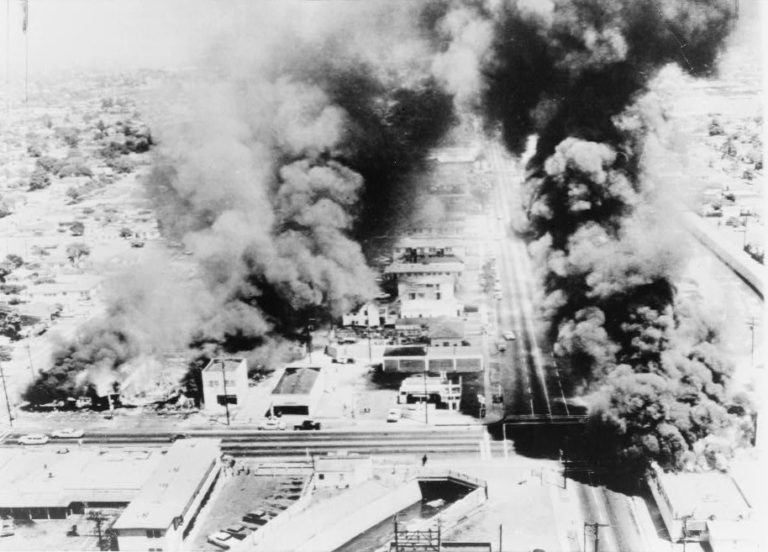
Debord in Watts: Race and Class Antagonisms Under Spectacle
In this paper, I explore Guy Debord’s analysis of race and racializing processes by closely examining the use of footage of the Watts rebellion in Debord’s film The Society of the Spectacle (1973), along with a close reading of Debord’s 1965 text on the uprising, “The Decline and Fall of the Spectacle-Commodity Economy.” Debord’s Marxist perspective on Watts understands the insurgents as potential revolutionary actors, primed for a “second proletarian assault against class society” (SotS, Thesis 47). To complicate Debord’s position, I look at the similarities and differences between his stance and the emergent theoretical paradigm of Afropessimism, which understands anti-black violence not as contingent upon capitalist alienation but instead as gratuitous violence required to uphold the figure of Humanity within civil society.