In this inaugural issue, Lateral takes the form of a cluster of four research threads. The initial threads converge around a consideration of knowledge formations, institutional and material location, and political intervention and implication. The initial four threads are meant as an exploration of what is possible and an invitation for further work. Theory and Method, curated by Patricia Clough, treats various forms of knowing and being in cultural studies research. Creative Industries, curated by Jaafar Aksikas, invites composite methodological approaches to intersectoral flows inside and outside the university. Universities in Question, curated by Bruce Burgett and Randy Martin, decenters established claims for disciplinary, labor, and political economic legitimations for higher education. Mobilisations, Interventions, and Cultural Policy curated by Emma Dowling, pursues current transformational activisms to rethink values of polity, policy, and participation.
Issue 1 (2012)
Culture Industries
Culture Industries: Critical Interventions
This thread presents a different agenda for studying culture and the culture industries in particular, one that is grounded in a distinctly cultural studies materialist reflexivity. Cultural studies is probably best understood as the politically committed, theoretically grounded, and radically self-reflexive and historical-materialist analysis of cultural processes and practices, where the commitment to imagine a humane, socialist society has always been a guiding assumption in the field from its early formations in post-war Britain.
“Nothing gold can stay:” Labor, Political Economy, and the Birmingham Legacy of the Culture Industries Debate
Over the course of the last 150 years or so, we can see three distinct phases of the culture industry. More specifically, there have been (at least) three eras marked by different configurations of the relationship between culture, politics, the dominant mode of production and the commodification of culture. Cultural Studies emerged from the second era, whose contours I’ll explore here; and we are now in a liminal phase brought on by the uncertain conflagration between the neoliberalism, convergence culture, and nascent popular uprisings under the banner (and hashtag) #occupyeverywhere. This third phase, or conjuncture, once again reconfigures these relations, making it important to revise the theoretical assumptions and political strategies that were adhered to in an earlier era of “the culture industry.” I will outline the direction I think this points to both in our understanding of the culture industries and in terms of political and theoretical strategy going forward.
Distributed Centralization: Web 2.0 as a Portal into Users’ Lives
Web 2.0 as a whole is beginning to take a decidedly interconnected shape. Facebook, Google, YouTube, Wikipedia, Blogger, Twitter and other Web 2.0 sites are linked to one another in a complex and bewildering array of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), user-created applications, links, protocols, and browser extensions. To trace these connections, this paper draws on the intersection between computing, software engineering, and the management of labor in informational capitalism to uncover an architectural model with which to understand this complexity: the portal model. We will see how the interconnections between Web 2.0 sites, built on de facto protocols, is creating the Web as Portal, an architecture built to capture value produced by users, value that was previously hidden as unstructured data. Web 2.0 as a portal is rife with contradictions: on the one hand, the Web (and Internet) remain distributed networks, and Web 2.0 applications could easily be mapped as distributed. On the other hand, extremely popular sites such as Facebook (for social networking) and Google (for search), as well as the increasing interconnection between them, are rendering Web 2.0 to be a centralized network. This distributed centralization is part of the larger portal architecture, wherein heterogeneous sites are articulated into a network of networks.
Mobilisations, Interventions, and Cultural Policy
Introduction: Mobilisations, Interventions, and Cultural Policy
There are four themes that weave their way through the research thread on Mobilisations, Interventions, and Cultural Policy in this issue. First, there is concern with intervention—intervention into the politics and practices of social movements and intervention into the academy and its traditions of knowledge production. Second, each text is situated firmly within a recognition and appreciation of social movements as knowledge producers. Third, all three contributions are unequivocally located in an urban context and the contemporary condition of inhabiting the city. Finally, what emerges from each reflection is a commitment to militant research and practice, as one that keeps ever-present an awareness of the relationship of research to existing material social relations of power and a commitment to confronting and transforming these very relations.
Urban Interventions / Intervenzione Urbane
Urban Interventions is a series of collages by Alexander Dellantonio that take the urban terrain with its rapid changes as the matrix of inquiry, presenting the artists reflections on the city. The strong colours used by the artist echo the city’s images, places, people and situations and tattered billboard posters and manifestos torn off the buildings the militants fly-posted them on are reassembled to show the city and its inhabitants in movement. Dellantonio appropriates parts of the city and seeks to return them to the spectator. In so doing, these works not only engage the urban terrain as a space of politics, they also raise questions about mediation in the context of the current crisis of political representation that is being expressed by movements across the world, whether for example in Tahrir or Syntagma Square, at Occupy Wall Street or during the public sector strikes in the UK.
Commentary on “Urban Interventions / Intervenzione Urbane”
Gavin Grindon responds to ‘Urban Interventions / Intervenzione Urbane’ by Alexander Dellantonio.
Commentary on “Urban Interventions / Intervenzione Urbane”
Begüm Özden Firat responds to ‘Urban Interventions / Intervenzione Urbane’ by Alexander Dellantonio.
Theory
Introduction: Theory and Method
The Theory and Method Thread of Lateral launches its first publication with two essays, one by John Mowitt of Cultural Studies and Comparative Literature at University of Minnesota and one by Jared Sexton, Director of African American Studies, School of Humanities at University of California Irvine. Together their essays along with responses by Christina Sharpe of American Studies at Tufts University, Adam Sitze of Black Studies and Law, Jurisprudence and Social Thought at Amherst College and Morgan Adamson of Cultural Studies and Comparative Literature at University of Minnesota, all take theory to one of the most pressing, worldly and yet intimate, of issues faced by each of us, whether working in and/or outside the academy: that is, the conditions of study, or studies, in the University.
The Humanities and the University in Ruin
Mowitt’s essay puts before us in terms of work or, as Mowitt puts it, ‘re: working’ the work of study, scholarship, and research under the contemporary conditions of ‘biopolitical contol’ or neoliberal structural adjustment of the academy. Mowitt warns against reducing the issue of study to complaints of poor pay and poor working conditions and therefore holds the issue of the labor of study on a fine line between the refusal of the work of study altogether and the insistence on simply enjoying the study that we are required to do or paid to do. Mowitt is not denying the poor conditions under which so many of us work for insufficient pay in and outside the University; he rather is warning us about moving too quickly off the fine line between refusal and enjoyment of the required or paid work of study. He is arguing instead for the value of study as a labor of the negative. Mowitt then takes some elegant last moves to turn this return to the labor of the negative into the work of affirmation, thought affirming itself; he thereby moves beyond the dialectic and the Euro-centric Hegelian tradition of progress to affirm instead the immanent unfolding of mindfulness or thoughtfulness, an unfolding of an affective labor that bears within it the in-excess of measure, the yet-incalculable excess of the current calculability of value. This makes the re: working of study not merely a matter of the human or the humanities but of the technical/human medium we fast are becoming, and which we are coming to know we always have been, as has the University.
Response to “The Humanities and the University in Ruin”
In his response to Mowitt, Morgan Adamson sharply reminds us that working conditions and remuneration for work, not to mention layoffs, hiring freezes and slashing of benefits, certainly are pressing concerns. Offering a quick survey of some of the horrid details of the work expected of research assistants in science labs, Adamson also softens the distinction implied in Mowitt’s focus on the humanities as against the sciences.
Response to “The Humanities and the University in Ruin”
Adam Sitze addresses the technological transformation of the academy, emphasized critically by Mowitt, which have put us beyond the troubles of discipline or disciplinarity to something more abstract and technical.
Ante-Anti-Blackness: Afterthoughts
Sexton sees to ask again about the tension between what has been coined afro- pessimism and black-optimism or what black intellectuals long have discussed as life after or in the social death of slavery. Taking up the arguments of a number of these intellectuals, especially those most recently offered by Fred Moten, Saidiya Hartman and Frank B. Wilderson, Sexton proposes that we stay on the fine line, here between optimism and pessimism, between life and death. For the optimists, the refusal of this identification is an insistence on ‘black agency being logically and ontologically prior’ to a social order that is anti-black, prior to a governance that turns blackness criminal and therefore calls for an affirmative politics of fugitivity. On the side of pessimism, is the longue duree of social death in the ongoing history of slavery and anti-black racism, if not racism generally. It is blackness theorized as ‘a structural position,’ ‘a conceptual framework,’ and ‘a structure of feeling.’ On the fine line between this pessimism and this optimism, Sexton argues that a question arises as to how to approach this social life in social death while enabling new means of thoughtfulness or mindfulness in living, in studying, in the University and elsewhere. Sexton borrowing from David Marriott argues for ‘the need to affirm affirmation through negation…not as a moral imperative…but as a psychopolitical necessity.’
Response to “Ante-Anti-Blackness”
In her response to Sexton, Christina Sharpe returns us to the psychopolitical necessity of such theorizing by pointing to her students who have organized again and again for black studies, and who in doing so each time also ask whether black studies ‘can ameliorate the quotidian experience of terror in black lives lived in an anti-black world?’ And if not, what should the relationship be between life and black studies, or between life and the University.
Universities in Question
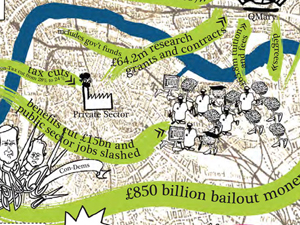
Countermapping the University
Appropriating the genre of the campus map, graduate students at Queen Mary University London and University of North Carolina Chapel Hill have produced a countermap of the university. Elegant in design, yet multi-purposed, their mapping of alternative uses and critiques takes the form of a poster-sized doubled sided print which locates the university within its larger societal force field (the map’s front side), and stages an arena for playing that field by means of a board game (which appears on the reverse side). In sharp contrast to the political geography of curricula intended to assimilate students to an already settled matter and progress-toward-a-degree, an unproblematic temporal beat measured by accumulated credit-hours, the critical cartographical work of this collective reallocates the energies of their seminars and research to produce alternate forms of knowledge and means for its legitimation.
Lateral Moves – Across Disciplines
“Lateral Moves – Across Disciplines” is an edited conversation with Randy Martin and three members of the Cultural Studies Praxis Collective (CSPC): Miriam Bartha, Diane Douglas, and Kanta Kochhar-Lindgren. The original conversation took place at the University of Washington’s Simpson Center for the Humanities in 2007. The transcript of the conversation was reworked and revised by the interlocutors and Bruce Burgett, the co-director (along with Kanta Kochhar-Lindgren) of the CSPC. The document as a whole surfaces and addresses a series of questions about interdisciplinarity, cultural studies, and the humanities; about creativity, agency, and advocacy; about different forms of professional, disciplinary, and civic education; and about knowledge, labor, and organizing.