Thy Phu’s Warring Visions: Photography and Vietnam draws on archives of the Vietnam War that center Vietnamese perspectives to complicate the historical and contemporary visual representation of Vietnamese identities that have been filtered through the Western narrative of the Vietnam War. Her book emphasizes the significance of typically denigrated visual materials including propaganda and vernacular photographs. She focuses on the complex deployment and reception of photographic objects as politicized symbols, sources of memorialization, and identity formation.
Keyword: war
Review of Television and the Afghan Culture Wars Brought to You by Foreigners, Warlords, and Activists by Wazhmah Osman (University of Illinois Press)
This review examines Wazhmah Osman’s book Television and the Afghan Culture Wars, an ethnographic study of television media in Afghanistan. The book explores the Afghan mediascape through richly detailed interviews with media industry professionals and local Afghans, which provide a realist portrayal of the perils and triumphs of media houses in Afghanistan, local cultural contestations, changing gender norms, and the role and reception of television in the nation’s rather tumultuous political and cultural life. Osman deflates the dominant notion in Western discourses of Afghanistan as a “hopeless landscape of powerless people,” (2) arguing that there is a thriving, internationally backed media infrastructure and a hopeful, culturally conscious citizenry in the nation. She argues that despite Afghanistan’s history of violence, ethnic tensions, atrocities against women, and imperialistic agendas by foreign powers, the Afghan media sector is a widely accessible platform for retribution against years of underdevelopment and war, with “the potential to underwrite democracy, national integration, and peace” (3).
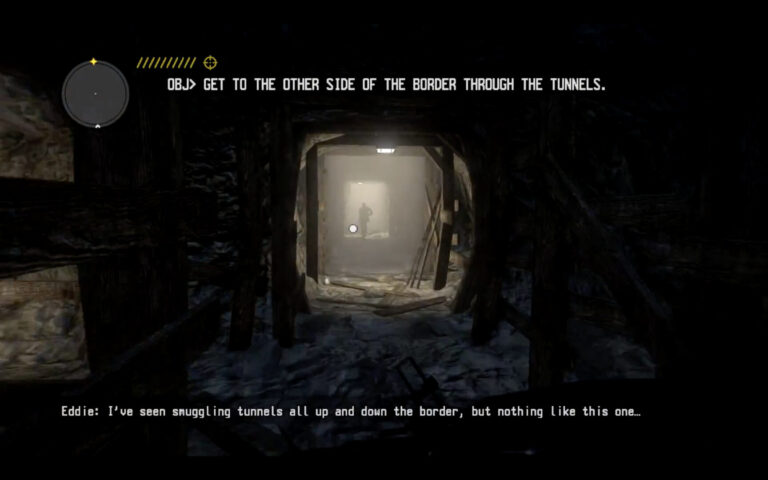
First-Person Shooters, Tunnel Warfare, and the Racial Infrastructures of the US–Mexico Border
Digital networked media actively participate in the nation-state’s and tech entrepreneurs’ efforts to imagine and manage the borderlands. These media facilitate virtual forms of thinking about the border both by offering popular reference points for the new technology being developed (e.g. Google Maps, Pokémon Go, Call of Duty) and by providing the actual tools through which these ideas can become actionable. This article analyzes one such reference point within the first-person shooter (FPS) console game Call of Juarez: The Cartel (Ubisoft, 2011). Like other border-themed video games, The Cartel borrows on colonial tropes and ideologies by creating playable narratives that invoke the untamable frontier and position racialized subjects as Other. Through its virtual modes of representation and interaction, the game encodes the racialization processes that continue to shape popular imaginings of the border. While its digital aesthetics animate a dynamic space of possibility, the logic of the first-person shooter reins in the expansiveness of animated space by restricting it to an interactive experience of tunnel warfare, an ideological orientation to the border underground that channels the players’ purposive motion into a space of direct confrontation and racial violence. Analyzing the narrative and procedural work of this ostensibly reactionary video game demonstrates how border infrastructures structure and shape specific forms of racial and colonial violence.
Review of Insurgent Aesthetics: Security and the Queer Life of the Forever War by Ronak K. Kapadia (Duke University Press)
Ronak K. Kapadia’s deeply conversant and well researched Insurgent Aesthetics: Security and the Queer Life of the Forever War brings queer, affect-oriented methodologies to bear on an analysis of Arab, Muslim, and South Asian diasporic art. It is these communities after all, Kapadia points out, who undergo increased scrutiny in the United States and Europe after September 11, 2001. According to the author, these diasporic artists engage in an insurgent aesthetic “against empire’s built sensorium,” which is a visual cultural practice that offers an alternative embodied critique of “US empire’s perverse logics of carcerality, security, and war” (10).
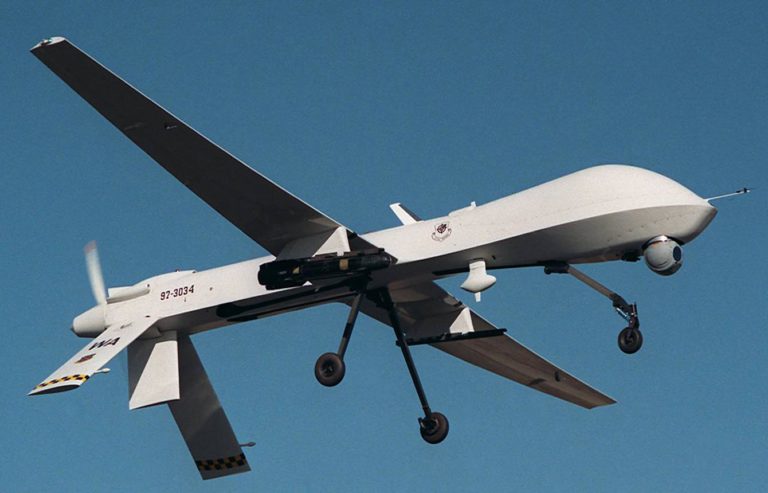
Killer Drones, Legal Ethics, and the Inconvenient Referent
I offer a close reading of the legal and political discourses by means of which the United States government recently has sought to legitimate its use of weaponized drones to carry out targeted assassinations of suspected anti-U.S. combatants abroad. Situating my analysis in the context of philosophical approaches to the problem of truth and linguistic reference, I examine official government speeches, legal documents, and reports of civilian casualties. My semiological critique of these texts is carried out both within and against the “humanitarian” framework of just war theory, my dual approach being necessitated by the twofold strategy of the government’s justificatory rhetoric: on the one hand, the government’s public discourse distorts the accepted meaning of certain unambiguous and pragmatically functional legal signifiers (the jus ad bellum use of terms such as self-defense, imminence, and necessity, for example); on the other hand, it exploits the uncertainty that is endemic to some of those very same terms (necessity and proportionality in particular) when they are used to refer to the jus in bello quantification and valuation of incommensurable variables—of, typically, a particular number of civilian casualties relative to the amount of “military advantage” to be derived from the attack that “unintentionally” produces those casualties.
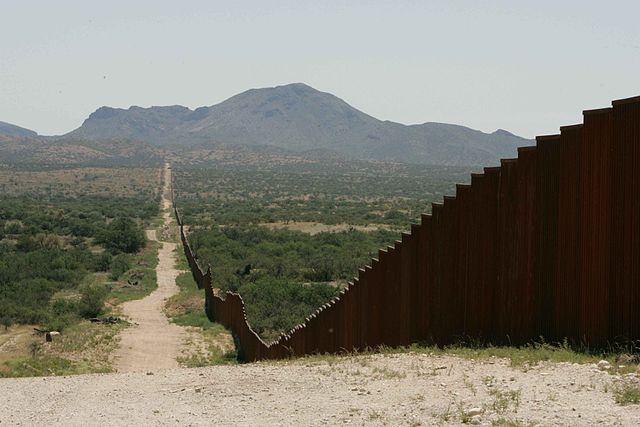
The Trump Wall: a Cultural Wall and a Cultural War
This essay decodes a Wall-DNA in American culture with an examination of two shaping moments in history, namely the Founding Fathers and the Mexican-American War. It argues that the Trump Wall, instead of protecting, endangers American values and opportunities; instead of uniting the nation, divides it and ignites cultural wars. The Trump Wall portends fear, bigotry, distrust, intolerance and disconnection; it is the Trump War. Therefore, this border construction is more of a mental construct than a physical one, especially when it involves a cultural re-landscaping and boundary shifting between the US and Mexico and within the two nations. The essay also challenges a one-dimensional and static view on American values, and calls for a 21st century sophistication for a culturally nuanced definition of what America means, and a 21st century agility to cross back and forth any walls without sparking a war.