As a “critical social theory,” intersectionality already lies at the roots of contemporary cultural studies, and the best work in cultural studies has the capacity for or is already engaging with intersectionality as method. This is work that accounts for the multifaceted nature of subjects, institutions, processes, and structures as it asks its questions about cultural objects, experience, ideology, history, or discourses. Intersectionality as, along with dialectical materialism, a core intellectual practice of cultural studies, offers expanded possibilities for political traction, relevance to the world and people’s lives, and transformative potential. We see models of such work throughout this issue, including with part two of a special forum on emergent analytics of critical humanities.
Issue 6.1 (Spring 2017)
Minor Miracles: Toward A Theory of Novelty in Aya of Yopougon
This essay undertakes a reparative reading of Aya of Yopougon, a multivolume graphic novel by Marguerite Abouet and Clément Oubrerie. Setting Aya alongside other African comics and prevailing interpretations of African and Diasporic literatures, this interpretation coins the term “novelty” to describe the unique mode of representing subjects, space, and time in the text. This “novelty” situates Aya at the intersection of tendencies in African, European, and North American comics art, and it juxtaposes subtle renditions of everyday life with overdetermined representations of African societies and Africans in Diaspora. The essay also articulates the relevance of novelty for feminist, queer, and postcolonial theories, comics scholarship, and Diaspora Studies.
Every Little Thing He Does: Entrepreneurship and Appropriation in the Magic Mike Series
This essay analyses the theatricalized performance of stripping in the popular films Magic Mike (2013; dir. Steven Soderbergh) and its sequel, Magic Mike XXL (2015; dir. Gregory Jacobs). Following a critical dance studies approach that attends to the intersection of body and gesture with socio-political, historical, and economic structures, I suggest theatricalized sexual labour in these films reveals the racial exclusions from the ideology of entrepreneurship. Considering the appropriation of black aesthetics in Magic Mike XXL’s performances of striptease, the film seeks to evaporate the spectre of race, that is, the way the white fantasy of the entrepreneurial subject is supported by the appropriation of racialized and especially black labour.
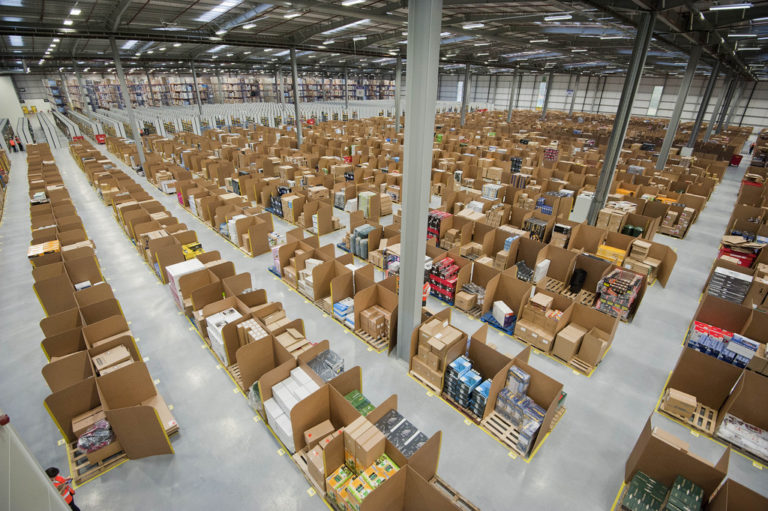
Target Markets and Logistical Management
This paper demonstrates how target marketing provides valuable point-of-sale and point-of-interaction insights, and argues that the labor theory of value is untenable for understanding the conditions of leisure-time surveillance and data aggregation. It then provides a close reading of an Amazon affiliated fulfillment center exposé in order to examine precisely how the information produced during leisure-time surveillance intensifies the exploitation of fulfillment center labor. Target marketing is part of a larger apparatus that aggregates data for the purposes of assigning risk, differentiating prices, and managing supply chains and labor costs.
Ethics, Collaboration, and Knowledge Production: Digital Storytelling with Sexually Diverse Farmworkers in California
This article outlines the digital storytelling methods used for a community based research project focused on issues of sexuality among California farmworkers: Sexualidades Campesinas. We note how our process of collaboration in the creation and production of digital stories was shaped by the context and our envisioned storytellers. We then offer a critical analysis of our own unique experience with digital storytelling in this project, focusing on a handful of concepts key to understanding the nature of our collaborative production process: community, affect and collaboration, storytelling, performance, and mediation, with an eye to the problem of ethics.
Forum: Emergent Critical Analytics for Alternative Humanities, Part II
Toward Alternative Humanities and Insurgent Collectivities
Introduction to Part II of the forum, Emergent Critical Analytics for Alternative Humanities. Here, emergent scholars respond to essays by J. Kēhaulani Kauanui, Kyla Wazana Tompkins, Julie Avril Minich, and Jodi Melamed, each of whom elaborated on the alternative possibilities of dealing with the legacies of settler colonialism, new materialisms, disability, and institutionality in Part I, published in Lateral 5.1.
Settler Colonialism
Ongoing Colonial Violence in Settler States
Response to J. Kēhaulani Kauanui, “A Structure, Not an Event: Settler Colonialism and Enduring Indigeneity,” published in Lateral 5.1. Jafri articulates how a critical race feminist/queer lens makes possible thinking that sees the repetitions of racialized, gendered, sexualized colonial violence.
The Times of Settler Colonialism
Response to J. Kēhaulani Kauanui, “A Structure, Not an Event: Settler Colonialism and Enduring Indigeneity,” published in Lateral 5.1. Gniadek approaches settler colonialism via questions of time—asking When is settler colonialism?—which reveals how narratives of national belonging tend to operate, as narrative confrontations that facilitate violence throughout and across time.
Thinking with Melissa Gniadek and Beenash Jafri
In “The Times of Settler Colonialism,” Melissa Gniadek urges me to go beyond the formulation of settler colonialism conceived as a problem of space. She pushes to further consider how Wolfe’s theorization of settler colonialism as structure (not an isolated episode) to examine “not only how histories of invasion do not stop, but also how…
New Materialist Philosophy
Exploring the Promise of New Materialisms
Response to Kyla Wazana Tompkins, “On the Limits and Promise of New Materialist Philosophy,” published in Lateral 5.1. Shomura mediates upon the promise and possibilities that new materialisms affords in its attentiveness to the material.
Rematerializations of Race
Response to Kyla Wazana Tompkins, “On the Limits and Promise of New Materialist Philosophy,” published in Lateral 5.1. Huang reassesses the methodological implications of new materialisms by grappling with renewed attention to form in literary studies to articulate the varying processes by which racial difference becomes elided, rematerialized, and remade.
Response to Michelle N. Huang and Chad Shomura
I am very grateful to Michelle N. Huang and Chad Shomura for their extensive engagement with my short and rather off-the-cuff thoughts on the limits and possibilities of new materialism. Their detailed and thoughtful responses extend and flesh out the work that I started to do in my original essay, taking my bullet-pointed aggravation with…
Critical Disability Studies
Critical Disability Studies as Methodology
Response to Julie Avril Minich, “Enabling Whom? Critical Disability Studies Now,” published in Lateral 5.1. Schalk calls for a shift in thinking that directly affects action and discusses creating classroom experiences that help students to critique intersecting social structures in their everyday encounters.
Toward a Crip-of-Color Critique: Thinking with Minich’s “Enabling Whom?”
Response to Julie Avril Minich, “Enabling Whom? Critical Disability Studies Now,” published in Lateral 5.1. Kim elaborates upon a crip-of-color critique, which has possibilities to both criticize structures that inherently devalue humans and to take action to work toward justice. Kim’s final call is to identify and act against the inequalities and harm of academic labor, urging readers to take seriously a “politics of refusal” that might help academics of color survive through alternative collectivities.
Thinking with Jina B. Kim and Sami Schalk
It is an honor and a privilege to read these careful and insightful responses to my provocation by Jina B. Kim and Sami Schalk, two intellectuals whose body of work, in my estimation, demonstrates exactly the kind of critical engagement I had in mind when I proposed the idea of critical disability studies as methodology…
Institutionality
The Contexts of Critique: Para-Institutions & the Multiple Lives of Institutionality in the Neoliberal University
Response to Jodi Melamed, “Proceduralism, Predisposing, Poesis: Forms of Institutionality, In the Making,” published in Lateral 5.1. Tabares invites us to question the role of what he calls ‘para-institutions,’ such as corporations, in shaping and influencing the logics and investments within the university. As a counterpoint to these processes, he ponders the possibilities of seizing upon the elements of proceduralism in mobilizing forms of collectivity that can span across institutional contexts outside the academy.
Neoliberalism, Racial Capitalism, and Liberal Democracy: Challenging an Emergent Critical Analytic
Response to Jodi Melamed, “Proceduralism, Predisposing, Poesis: Forms of Institutionality, In the Making,” published in Lateral 5.1. Aho pointedly argues that studies of institutionality all too often substantiate what she calls neoliberalocentrism, which readily posits neoliberalism as the singular paradigm into narrating a teleological development of history. Instead, she echoes Kim and Schalk to articulate ‘crip-of-color materialism’ as an analytic that thickens understandings about global structures of inequity and fissures within them.
Response to Tanja Aho and Leland Tabares: Madness and Parainstitutionality
Tanja Aho’s response both criticizes a scholarly trend she identifies as “neoliberalcentrist analytics” for presuming neoliberalism’s homogeny, hegemony, and totality and introduces a new critical analytic, “crip of color materialism,” which Aho describes as “the convergence of a historical materialist critical disability studies/crip theory/mad studies with critical race theory and queer of color critique.” This…